Safe navigation is impossible without Aids to Navigation (AtoN) solutions. At the core of this, marine buoys are one of the main aids to navigation. Provided in different designs based on the International Organization for Marine Aids to Navigation (IALA), marine buoys act as a guide to ensure safe navigation. Accordingly, the durability and performance of these buoys are more vital than ever thought. Besides design, production methods, and other factors that impact the durability and performance of buoys, the material used in their manufacture is a determining factor. So, in this blog post we compare polyethylene vs steel buoys.
Polyethylene (PE) and steel are two common and primary materials mostly used in the manufacturing of marine buoys, of which we delve into a deep comparison to answer the question: which material is better for buoys as aids to navigation?
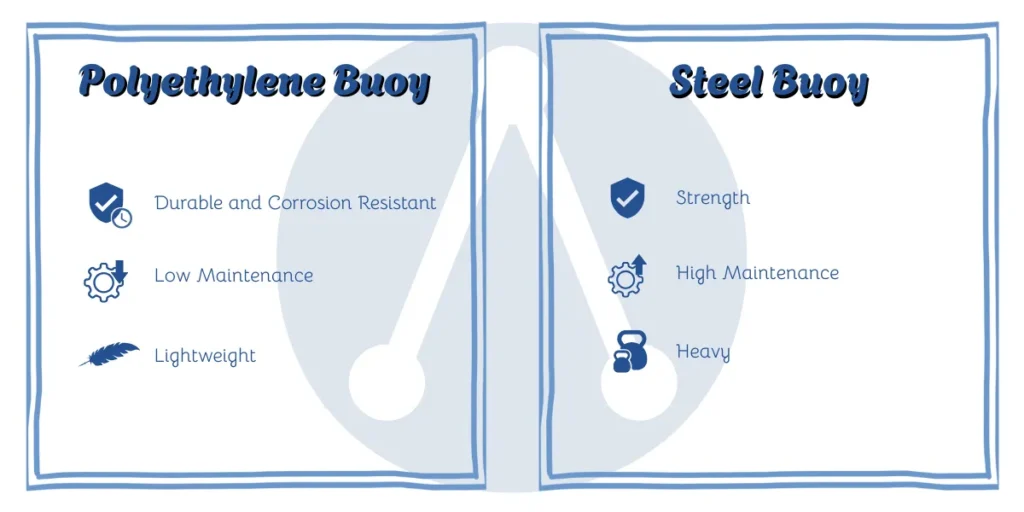
A Comparison of Polyethylene vs Steel Buoys
Polyethylene (PE) is a versatile type of plastic, created by polymerizing ethylene. Due to its superior lightweight and durability, polyethylene is widely used in the design of marine buoys. Steel, on the other hand, is a lightweight but resistant metal that can meet the necessary features of a buoy. These two materials have always been in a battle over which one is better. Here, we compare them based on the critical factors that can lead to better decision-making.
See also: “7 Types of Navigation Buoys“
Durability and Resistance

Due to the critical role of marine buoys as Aids to Navigation, they must be durable enough to be efficient in all conditions. Polyethylene is typically used because of its significant durability, offering high resistance to UV radiation, corrosion, and cracks. Steel is another durable material that provides high strength and resistance to deformation. But when it comes to comparison, polyethylene offers more durability, and the risks of corrosion affected by environmental factors are higher in steel buoys (e.g., rust, coating degradation, or discoloration).
Weight, Buoyancy, and Handling
In terms of buoyancy, steel offers heavy weights that challenge buoyancy, handling, and deployment processes. Conversely, the superior lightweight of polyethylene buoys guarantees their high buoyancy and straightforwardness of handling. To maximize their efficiency in harsh marine conditions, polyethylene buoys are typically anchored or fixed to the seabed. Therefore, strong currents and waves cannot move the buoy.
Maintenance Requirements

Maintenance and lifecycle costs have always been one of the main concerns in every project. Polyethylene buoys are provided in the requested color without needing any painting or coatings. Steel buoys should be coated with a paint layer, which can be degraded over time due to UV radiation and environmental impacts.
So, polyethylene buoys require less maintenance than steel buoys, which eventually results in lower maintenance costs. Moreover, polyethylene navigation buoys, manufactured by the Rotational Molding (Rotomolding) method, are provided in single-piece units. In contrast, steel navigation buoys are designed using welding methods, which require regular maintenance to ensure the integrity of the welded areas.
Applications and Performance
According to the high durability of polyethylene buoys, they provide more reliability in harsh marine conditions and in projects where the performance of the buoy is of high importance (e.g., ports). Beyond these cases, the risk of steel navigation buoys failing overall is higher because of the deformation, sinking, and rusting, which minimize their performance and efficiency. However, polyethylene buoys offer safer marinas with their optimized performance, whether they are used in offshore or inshore environments.
What Is the Best Material for a Buoy? Plastic vs Steel Buoy

Let’s delve into the advantages and disadvantages of each material to decide on which one is the best for a buoy. Steel is a strong, durable material that can be used in heavy-duty projects and harsh conditions. But their high performance depends on regular maintenance, well galvanization, and reliable welding. Otherwise, steel navigation buoys are failed affected by environmental impacts, crashes, and consistent UV radiation. So, their strength and durability are the top advantages of steel buoys, while regular maintenance requirements and heavy weight can be their disadvantages.
Polyethylene buoys, on the other hand, offer UV and corrosion resistance and high durability in harsh marine conditions, which makes them a suitable solution for heavy-duty projects. Their lightweight also provides perfect buoyancy even in strong currents and wavy environments. In addition, polyethylene navigation buoys are designed in single-piece units with the color in the resin and do not require painting, coating, or welding. Therefore, low maintenance requirements, high buoyancy, lightweight, and high durability and resistance can be mentioned as polyethylene buoys’ advantages. However, polyethylene is at risk of failing in some extreme offshore conditions due to its lower strength rather than the steel buoys.
But is polyethylene harmful to humans? Polyethylene is the most common plastic in the world, which is used for food containers, water pipes, and medical packaging beyond its application in the marine industry. It is chemically inert and does not release harmful or toxic particles. However, polyethylene is categorized based on its density level and molecular structure. Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) offers more flexibility, low strength, and a soft surface. Medium-Density Polyethylene (MDPE) provides a balance of strength and flexibility with perfect resistance. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) includes high rigidity and proven resistance, which is the most sustainable type of polyethylene.
ADOR’s Buoys as a High-End Solution

Due to the benefits of polyethylene over steel, ADOR provides highly qualified MDPE and HDPE polyethylene buoys manufactured by Rotational Molding (Rotomolding) to design single-piece units based on the IALA standards. ADOR’s buoys (and all product ranges) are provided with a highly customizable design based on the project specifications and environmental conditions to optimize the buoys’ efficiency further. This combination of technical approach and engineered solutions ensures that our marine buoys offer high performance and superior durability even in harsh conditions.
Conclusion
In summary, marine buoys are vital elements of Aids to Navigation (AtoN) that allow for safe navigation. Due to their highly important role, buoys must be durable, resistant, buoyant, and highly visible. This is why polyethylene (PE) and steel, as the two most common materials used in marine buoys, have always been in a battle to prove which one is the best. Polyethylene offers high durability, UV and corrosion resistance, lightweight, and perfect buoyancy.
Steel navigation buoys, on the other hand, offer high strength and durability in structure, but are heavyweight and require regular maintenance to prevent discoloring, deformation, and rusting. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of polyethylene and steel buoys provides a better insight into each application range and performance in different conditions, which allows for better decision-making and investment.




